-
1 current regime
-
2 current regime
Деловая лексика: нынешний режим -
3 current regime
-
4 current-carrying capacity
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
предельно допустимый ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
прочность печатной платы к токовой нагрузке
Свойство печатной платы сохранять электрические и механические характеристики после воздействия максимально допустимой токовой нагрузки на печатный проводник или металлизированное отверстие печатной платы.
[ ГОСТ Р 53386-2009]Тематики
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > current-carrying capacity
-
5 current sanctions regime
Внешняя политика: действующий санкционный режим (англ. термин взят из статьи в газете Washington Post)Универсальный англо-русский словарь > current sanctions regime
-
6 bed regime
-
7 constant voltage to constant current crossover
переход от постоянного напряжения к постоянному току
-
[IEV number 314-05-09]EN
constant voltage to constant current crossover
behaviour of a stabilized power supply that automatically converts the mode of operation from voltage stabilization to current stabilization when the output current reaches a preset value, and vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]FR
transition tension constante à courant constant
comportement d'une alimentation qui convertit automatiquement le régime de stabilisation en tension en régime de stabilisation en courant lorsque le courant de sortie atteint une valeur préréglée et vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > constant voltage to constant current crossover
-
8 facteur de régime cyclique
коэффициент циклической токовой нагрузки (кабелей)
Коэффициент, на который может быть умножен номинальный ток установившегося режима, соответствующий коэффициенту нагрузки 100 %, для получения допустимого пикового значения тока в течение суточного цикла, при котором температура токопроводящей жилы в течение этого цикла достигает, но не превышает максимально допустимое значение
[IEV number 461-23-02]EN
cyclic rating factor
factor by which the permissible steady-state rated current corresponding to a 100 % load factor may be multiplied to obtain the permissible peak value of current during a daily cycle such that the conductor attains, but does not exceed, the maximum rated temperature during the cycle
[IEV number 461-23-02]FR
facteur de régime cyclique
facteur par lequel le courant assigné admissible en régime permanent, correspondant à un facteur de charge 100 %, peut être multiplié pour obtenir la valeur de pointe du courant au cours d'un cycle journalier, de sorte qu'au cours de ce cycle, l'âme atteigne sans la dépasser la température assignée maximale
[IEV number 461-23-02]Тематики
- кабели, провода...
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > facteur de régime cyclique
-
9 continuous current-carrying capacity
длительная пропускная способность по току
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current-carrying capacity
-
10 continuous current
(длительный) допустимый ток
Максимальное значение электрического тока, который может протекать длительно по проводнику, устройству или аппарату при определенных условиях без превышения определенного значения их температуры в установившемся режиме
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]
Этот ток обозначают IZ
[ ГОСТ Р 50571. 1-2009 ( МЭК 60364-1: 2005)]EN
(continuous) current-carrying capacity
ampacity (US)
maximum value of electric current which can be carried continuously by a conductor, a device or an apparatus, under specified conditions without its steady-state temperature exceeding a specified value
[IEV number 826-11-13]
ampacity
The current in amperes that a conductor can carry continuously under the conditions of use without exceeding its temperature rating.
[National Electrical Cod]FR
courant (permanent) admissible, m
valeur maximale du courant électrique qui peut parcourir en permanence, un conducteur, un dispositif ou un appareil, sans que sa température de régime permanent, dans des conditions données, soit supérieure à la valeur spécifiée
[IEV number 826-11-13]Ampacity, the term is defined as the maximum amount of current a cable can carry before sustaining immediate or progressive deterioration. Also described as current rating or current-carrying capacity, is the RMS electric current which a device can continuously carry while remaining within its temperature rating. The ampacity of a cable depends on:
- its insulation temperature rating;
- conductor electrical properties for current;
- frequency, in the case of alternating currents;
- ability to dissipate heat, which depends on cable geometry and its surroundings;
- ambient temperature.
Electric wires have some resistance, and electric current flowing through them causes voltage drop and power dissipation, which heats the cable. Copper or aluminum can conduct a large amount of current before melting, but long before the conductors melt, their insulation would be damaged by the heat.
The ampacity for a power cable is thus based on physical and electrical properties of the material & construction of the conductor and of its insulation, ambient temperature, and environmental conditions adjacent to the cable. Having a large overall surface area may dissipate heat well if the environment can absorb the heat.
In a long run of cable, different conditions govern, and installation regulations normally specify that the most severe condition along the run governs the cable's rating. Cables run in wet or oily locations may carry a lower temperature rating than in a dry installation. Derating is necessary for multiple circuits in close proximity. When multiple cables are near, each contributes heat to the others and diminishes the amount of cooling air that can flow past the individual cables. The overall ampacity of the insulated conductors in a bundle of more than 3 must be derated, whether in a raceway or cable. Usually the de-rating factor is tabulated in a nation's wiring regulations.
Depending on the type of insulating material, common maximum allowable temperatures at the surface of the conductor are 60, 75 and 90 degrees Celsius, often with an ambient air temperature of 30°C. In the U.S., 105°C is allowed with ambient of 40°C, for larger power cables, especially those operating at more than 2 kV. Likewise, specific insulations are rated 150, 200 or 250°C.
The allowed current in cables generally needs to be decreased (derated) when the cable is covered with fireproofing material.
For example, the United States National Electric Code, Table 310-16, specifies that up to three 8 AWG copper wires having a common insulating material (THWN) in a raceway, cable, or direct burial has an ampacity of 50 A when the ambient air is 30°C, the conductor surface temperature allowed to be 75°C. A single insulated conductor in air has 70 A rating.
Ampacity rating is normally for continuous current, and short periods of overcurrent occur without harm in most cabling systems. The acceptable magnitude and duration of overcurrent is a more complex topic than ampacity.
When designing an electrical system, one will normally need to know the current rating for the following:- Wires
- Printed Circuit Board traces, where included
- Fuses
- Circuit breakers
- All or nearly all components used
Some devices are limited by power rating, and when this power rating occurs below their current limit, it is not necessary to know the current limit to design a system. A common example of this is lightbulb holders.
[http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ampacity]
Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
Синонимы
EN
DE
- Dauerstrombelastbarkeit, f
- Strombelastbarkeit, f
FR
- courant admissible, m
- courant permanent admissible, m
непрерывный ток
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > continuous current
-
11 inrush current
пусковой ток
-EN
inrush current
transient current associated with energizing of transformers, cables, reactors, etc
[IEV number 448-11-30]
inrush current
Iin
current occurring during the transient period from the moment of switching to the steady-state condition
[IEC 60738-1, ed. 3.0 (2006-04)]
starting current
the steady-state r.m.s. current taken from the line over the starting period from zero speed to load speed with rated voltage and frequency applied
[IEV number 411-48-18]FR
courant d'appel
courant transitoire associé à la mise sous tension des transformateurs, câbles, bobines d'inductance, etc
[IEV number 448-11-30]
courant de démarrage
valeur efficace du courant en régime établi, absorbé par le moteur pendant la période de démarrage de la vitesse nulle jusqu'à la vitesse de charge minimale lorsqu'il est alimenté à la tension et à la fréquence assignées
[IEV number 411-48-18]Тематики
- машины электрические вращающиеся в целом
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
ток пусковой мощности
(напр. турбины)
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
1.3.9 пусковой ток (inrush current): Кратковременный высокий ток лампы, полностью или частично выпрямленный, при асимметричном нагреве электродов в течение нескольких секунд при зажигании лампы.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53075-2008: Лампы металлогалогенные. Эксплуатационные требования оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > inrush current
-
12 starting current
пусковой ток
-EN
inrush current
transient current associated with energizing of transformers, cables, reactors, etc
[IEV number 448-11-30]
inrush current
Iin
current occurring during the transient period from the moment of switching to the steady-state condition
[IEC 60738-1, ed. 3.0 (2006-04)]
starting current
the steady-state r.m.s. current taken from the line over the starting period from zero speed to load speed with rated voltage and frequency applied
[IEV number 411-48-18]FR
courant d'appel
courant transitoire associé à la mise sous tension des transformateurs, câbles, bobines d'inductance, etc
[IEV number 448-11-30]
courant de démarrage
valeur efficace du courant en régime établi, absorbé par le moteur pendant la période de démarrage de la vitesse nulle jusqu'à la vitesse de charge minimale lorsqu'il est alimenté à la tension et à la fréquence assignées
[IEV number 411-48-18]Тематики
- машины электрические вращающиеся в целом
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > starting current
-
13 limited-current source
источник с ограничением тока
Источник электрической энергии для электрической цепи с ограничением возможного значения тока до безопасного уровня, имеющий электрическое разделение между своим выходом и опасными токоведущими частями.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-195-2005]
источник с ограничением тока
Устройство, питающее электрическую цепь электрической энергией, которое при этом:
- обеспечивает ток установившегося (постоянного) значения и электрический разряд, ограниченный до неопасного уровня, и
- оборудовано электрическим защитным разделением между выходом устройства и любой опасной токоведущей частью.
[ ГОСТ Р МЭК 60050-826-2009]EN
limited-current source
device supplying electric energy to an electric circuit:
– with a steady-state current and an electric charge limited to non-hazardous levels, and
– equipped with electrically protective separation between the output of the device and any hazardous-live-part
[IEV number 195-06-20]FR
source à courant limité
appareil qui fournit de l'énergie électrique à un circuit électrique:
– avec un courant et une charge en régime permanent limités à des niveaux non dangereux et
– avec une séparation de protection électrique entre la sortie de l'appareil et les parties actives dangereuses
[IEV number 195-06-20]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > limited-current source
-
14 near cash
!гос. фин. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.This paper provides background information on the framework for the planning and control of public expenditure in the UK which has been operated since the 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR). It sets out the different classifications of spending for budgeting purposes and why these distinctions have been adopted. It discusses how the public expenditure framework is designed to ensure both sound public finances and an outcome-focused approach to public expenditure.The UK's public spending framework is based on several key principles:"consistency with a long-term, prudent and transparent regime for managing the public finances as a whole;" "the judgement of success by policy outcomes rather than resource inputs;" "strong incentives for departments and their partners in service delivery to plan over several years and plan together where appropriate so as to deliver better public services with greater cost effectiveness; and"the proper costing and management of capital assets to provide the right incentives for public investment.The Government sets policy to meet two firm fiscal rules:"the Golden Rule states that over the economic cycle, the Government will borrow only to invest and not to fund current spending; and"the Sustainable Investment Rule states that net public debt as a proportion of GDP will be held over the economic cycle at a stable and prudent level. Other things being equal, net debt will be maintained below 40 per cent of GDP over the economic cycle.Achievement of the fiscal rules is assessed by reference to the national accounts, which are produced by the Office for National Statistics, acting as an independent agency. The Government sets its spending envelope to comply with these fiscal rules.Departmental Expenditure Limits ( DEL) and Annually Managed Expenditure (AME)"Departmental Expenditure Limit ( DEL) spending, which is planned and controlled on a three year basis in Spending Reviews; and"Annually Managed Expenditure ( AME), which is expenditure which cannot reasonably be subject to firm, multi-year limits in the same way as DEL. AME includes social security benefits, local authority self-financed expenditure, debt interest, and payments to EU institutions.More information about DEL and AME is set out below.In Spending Reviews, firm DEL plans are set for departments for three years. To ensure consistency with the Government's fiscal rules departments are set separate resource (current) and capital budgets. The resource budget contains a separate control total for “near cash” expenditure, that is expenditure such as pay and current grants which impacts directly on the measure of the golden rule.To encourage departments to plan over the medium term departments may carry forward unspent DEL provision from one year into the next and, subject to the normal tests for tautness and realism of plans, may be drawn down in future years. This end-year flexibility also removes any incentive for departments to use up their provision as the year end approaches with less regard to value for money. For the full benefits of this flexibility and of three year plans to feed through into improved public service delivery, end-year flexibility and three year budgets should be cascaded from departments to executive agencies and other budget holders.Three year budgets and end-year flexibility give those managing public services the stability to plan their operations on a sensible time scale. Further, the system means that departments cannot seek to bid up funds each year (before 1997, three year plans were set and reviewed in annual Public Expenditure Surveys). So the credibility of medium-term plans has been enhanced at both central and departmental level.Departments have certainty over the budgetary allocation over the medium term and these multi-year DEL plans are strictly enforced. Departments are expected to prioritise competing pressures and fund these within their overall annual limits, as set in Spending Reviews. So the DEL system provides a strong incentive to control costs and maximise value for money.There is a small centrally held DEL Reserve. Support from the Reserve is available only for genuinely unforeseeable contingencies which departments cannot be expected to manage within their DEL.AME typically consists of programmes which are large, volatile and demand-led, and which therefore cannot reasonably be subject to firm multi-year limits. The biggest single element is social security spending. Other items include tax credits, Local Authority Self Financed Expenditure, Scottish Executive spending financed by non-domestic rates, and spending financed from the proceeds of the National Lottery.AME is reviewed twice a year as part of the Budget and Pre-Budget Report process reflecting the close integration of the tax and benefit system, which was enhanced by the introduction of tax credits.AME is not subject to the same three year expenditure limits as DEL, but is still part of the overall envelope for public expenditure. Affordability is taken into account when policy decisions affecting AME are made. The Government has committed itself not to take policy measures which are likely to have the effect of increasing social security or other elements of AME without taking steps to ensure that the effects of those decisions can be accommodated prudently within the Government's fiscal rules.Given an overall envelope for public spending, forecasts of AME affect the level of resources available for DEL spending. Cautious estimates and the AME margin are built in to these AME forecasts and reduce the risk of overspending on AME.Together, DEL plus AME sum to Total Managed Expenditure (TME). TME is a measure drawn from national accounts. It represents the current and capital spending of the public sector. The public sector is made up of central government, local government and public corporations.Resource and Capital Budgets are set in terms of accruals information. Accruals information measures resources as they are consumed rather than when the cash is paid. So for example the Resource Budget includes a charge for depreciation, a measure of the consumption or wearing out of capital assets."Non cash charges in budgets do not impact directly on the fiscal framework. That may be because the national accounts use a different way of measuring the same thing, for example in the case of the depreciation of departmental assets. Or it may be that the national accounts measure something different: for example, resource budgets include a cost of capital charge reflecting the opportunity cost of holding capital; the national accounts include debt interest."Within the Resource Budget DEL, departments have separate controls on:"Near cash spending, the sub set of Resource Budgets which impacts directly on the Golden Rule; and"The amount of their Resource Budget DEL that departments may spend on running themselves (e.g. paying most civil servants’ salaries) is limited by Administration Budgets, which are set in Spending Reviews. Administration Budgets are used to ensure that as much money as practicable is available for front line services and programmes. These budgets also help to drive efficiency improvements in departments’ own activities. Administration Budgets exclude the costs of frontline services delivered directly by departments.The Budget preceding a Spending Review sets an overall envelope for public spending that is consistent with the fiscal rules for the period covered by the Spending Review. In the Spending Review, the Budget AME forecast for year one of the Spending Review period is updated, and AME forecasts are made for the later years of the Spending Review period.The 1998 Comprehensive Spending Review ( CSR), which was published in July 1998, was a comprehensive review of departmental aims and objectives alongside a zero-based analysis of each spending programme to determine the best way of delivering the Government's objectives. The 1998 CSR allocated substantial additional resources to the Government's key priorities, particularly education and health, for the three year period from 1999-2000 to 2001-02.Delivering better public services does not just depend on how much money the Government spends, but also on how well it spends it. Therefore the 1998 CSR introduced Public Service Agreements (PSAs). Each major government department was given its own PSA setting out clear targets for achievements in terms of public service improvements.The 1998 CSR also introduced the DEL/ AME framework for the control of public spending, and made other framework changes. Building on the investment and reforms delivered by the 1998 CSR, successive spending reviews in 2000, 2002 and 2004 have:"provided significant increase in resources for the Government’s priorities, in particular health and education, and cross-cutting themes such as raising productivity; extending opportunity; and building strong and secure communities;" "enabled the Government significantly to increase investment in public assets and address the legacy of under investment from past decades. Departmental Investment Strategies were introduced in SR2000. As a result there has been a steady increase in public sector net investment from less than ¾ of a per cent of GDP in 1997-98 to 2¼ per cent of GDP in 2005-06, providing better infrastructure across public services;" "introduced further refinements to the performance management framework. PSA targets have been reduced in number over successive spending reviews from around 300 to 110 to give greater focus to the Government’s highest priorities. The targets have become increasingly outcome-focused to deliver further improvements in key areas of public service delivery across Government. They have also been refined in line with the conclusions of the Devolving Decision Making Review to provide a framework which encourages greater devolution and local flexibility. Technical Notes were introduced in SR2000 explaining how performance against each PSA target will be measured; and"not only allocated near cash spending to departments, but also – since SR2002 - set Resource DEL plans for non cash spending.To identify what further investments and reforms are needed to equip the UK for the global challenges of the decade ahead, on 19 July 2005 the Chief Secretary to the Treasury announced that the Government intends to launch a second Comprehensive Spending Review (CSR) reporting in 2007.A decade on from the first CSR, the 2007 CSR will represent a long-term and fundamental review of government expenditure. It will cover departmental allocations for 2008-09, 2009-10 and 2010 11. Allocations for 2007-08 will be held to the agreed figures already announced by the 2004 Spending Review. To provide a rigorous analytical framework for these departmental allocations, the Government will be taking forward a programme of preparatory work over 2006 involving:"an assessment of what the sustained increases in spending and reforms to public service delivery have achieved since the first CSR. The assessment will inform the setting of new objectives for the decade ahead;" "an examination of the key long-term trends and challenges that will shape the next decade – including demographic and socio-economic change, globalisation, climate and environmental change, global insecurity and technological change – together with an assessment of how public services will need to respond;" "to release the resources needed to address these challenges, and to continue to secure maximum value for money from public spending over the CSR period, a set of zero-based reviews of departments’ baseline expenditure to assess its effectiveness in delivering the Government’s long-term objectives; together with"further development of the efficiency programme, building on the cross cutting areas identified in the Gershon Review, to embed and extend ongoing efficiency savings into departmental expenditure planning.The 2007 CSR also offers the opportunity to continue to refine the PSA framework so that it drives effective delivery and the attainment of ambitious national standards.Public Service Agreements (PSAs) were introduced in the 1998 CSR. They set out agreed targets detailing the outputs and outcomes departments are expected to deliver with the resources allocated to them. The new spending regime places a strong emphasis on outcome targets, for example in providing for better health and higher educational standards or service standards. The introduction in SR2004 of PSA ‘standards’ will ensure that high standards in priority areas are maintained.The Government monitors progress against PSA targets, and departments report in detail twice a year in their annual Departmental Reports (published in spring) and in their autumn performance reports. These reports provide Parliament and the public with regular updates on departments’ performance against their targets.Technical Notes explain how performance against each PSA target will be measured.To make the most of both new investment and existing assets, there needs to be a coherent long term strategy against which investment decisions are taken. Departmental Investment Strategies (DIS) set out each department's plans to deliver the scale and quality of capital stock needed to underpin its objectives. The DIS includes information about the department's existing capital stock and future plans for that stock, as well as plans for new investment. It also sets out the systems that the department has in place to ensure that it delivers its capital programmes effectively.This document was updated on 19 December 2005.Near-cash resource expenditure that has a related cash implication, even though the timing of the cash payment may be slightly different. For example, expenditure on gas or electricity supply is incurred as the fuel is used, though the cash payment might be made in arrears on aquarterly basis. Other examples of near-cash expenditure are: pay, rental.Net cash requirement the upper limit agreed by Parliament on the cash which a department may draw from theConsolidated Fund to finance the expenditure within the ambit of its Request forResources. It is equal to the agreed amount of net resources and net capital less non-cashitems and working capital.Non-cash cost costs where there is no cash transaction but which are included in a body’s accounts (or taken into account in charging for a service) to establish the true cost of all the resourcesused.Non-departmental a body which has a role in the processes of government, but is not a government public body, NDPBdepartment or part of one. NDPBs accordingly operate at arm’s length from governmentMinisters.Notional cost of a cost which is taken into account in setting fees and charges to improve comparability with insuranceprivate sector service providers.The charge takes account of the fact that public bodies donot generally pay an insurance premium to a commercial insurer.the independent body responsible for collecting and publishing official statistics about theUK’s society and economy. (At the time of going to print legislation was progressing tochange this body to the Statistics Board).Office of Government an office of the Treasury, with a status similar to that of an agency, which aims to maximise Commerce, OGCthe government’s purchasing power for routine items and combine professional expertiseto bear on capital projects.Office of the the government department responsible for discharging the Paymaster General’s statutoryPaymaster General,responsibilities to hold accounts and make payments for government departments and OPGother public bodies.Orange bookthe informal title for Management of Risks: Principles and Concepts, which is published by theTreasury for the guidance of public sector bodies.Office for NationalStatistics, ONS60Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————"GLOSSARYOverdraftan account with a negative balance.Parliament’s formal agreement to authorise an activity or expenditure.Prerogative powerspowers exercisable under the Royal Prerogative, ie powers which are unique to the Crown,as contrasted with common-law powers which may be available to the Crown on the samebasis as to natural persons.Primary legislationActs which have been passed by the Westminster Parliament and, where they haveappropriate powers, the Scottish Parliament and the Northern Ireland Assembly. Begin asBills until they have received Royal Assent.arrangements under which a public sector organisation contracts with a private sectorentity to construct a facility and provide associated services of a specified quality over asustained period. See annex 7.5.Proprietythe principle that patterns of resource consumption should respect Parliament’s intentions,conventions and control procedures, including any laid down by the PAC. See box 2.4.Public Accountssee Committee of Public Accounts.CommitteePublic corporationa trading body controlled by central government, local authority or other publiccorporation that has substantial day to day operating independence. See section 7.8.Public Dividend finance provided by government to public sector bodies as an equity stake; an alternative to Capital, PDCloan finance.Public Service sets out what the public can expect the government to deliver with its resources. EveryAgreement, PSAlarge government department has PSA(s) which specify deliverables as targets or aimsrelated to objectives.a structured arrangement between a public sector and a private sector organisation tosecure an outcome delivering good value for money for the public sector. It is classified tothe public or private sector according to which has more control.Rate of returnthe financial remuneration delivered by a particular project or enterprise, expressed as apercentage of the net assets employed.Regularitythe principle that resource consumption should accord with the relevant legislation, therelevant delegated authority and this document. See box 2.4.Request for the functional level into which departmental Estimates may be split. RfRs contain a number Resources, RfRof functions being carried out by the department in pursuit of one or more of thatdepartment’s objectives.Resource accountan accruals account produced in line with the Financial Reporting Manual (FReM).Resource accountingthe system under which budgets, Estimates and accounts are constructed in a similar wayto commercial audited accounts, so that both plans and records of expenditure allow in fullfor the goods and services which are to be, or have been, consumed – ie not just the cashexpended.Resource budgetthe means by which the government plans and controls the expenditure of resources tomeet its objectives.Restitutiona legal concept which allows money and property to be returned to its rightful owner. Ittypically operates where another person can be said to have been unjustly enriched byreceiving such monies.Return on capital the ratio of profit to capital employed of an accounting entity during an identified period.employed, ROCEVarious measures of profit and of capital employed may be used in calculating the ratio.Public Privatepartnership, PPPPrivate Finance Initiative, PFIParliamentaryauthority61Managing Public Money"————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARYRoyal charterthe document setting out the powers and constitution of a corporation established underprerogative power of the monarch acting on Privy Council advice.Second readingthe second formal time that a House of Parliament may debate a bill, although in practicethe first substantive debate on its content. If successful, it is deemed to denoteParliamentary approval of the principle of the proposed legislation.Secondary legislationlaws, including orders and regulations, which are made using powers in primary legislation.Normally used to set out technical and administrative provision in greater detail thanprimary legislation, they are subject to a less intense level of scrutiny in Parliament.European legislation is,however,often implemented in secondary legislation using powers inthe European Communities Act 1972.Service-level agreement between parties, setting out in detail the level of service to be performed.agreementWhere agreements are between central government bodies, they are not legally a contractbut have a similar function.Shareholder Executive a body created to improve the government’s performance as a shareholder in businesses.Spending reviewsets out the key improvements in public services that the public can expect over a givenperiod. It includes a thorough review of departmental aims and objectives to find the bestway of delivering the government’s objectives, and sets out the spending plans for the givenperiod.State aidstate support for a domestic body or company which could distort EU competition and sois not usually allowed. See annex 4.9.Statement of Excessa formal statement detailing departments’ overspends prepared by the Comptroller andAuditor General as a result of undertaking annual audits.Statement on Internal an annual statement that Accounting Officers are required to make as part of the accounts Control, SICon a range of risk and control issues.Subheadindividual elements of departmental expenditure identifiable in Estimates as single cells, forexample cell A1 being administration costs within a particular line of departmental spending.Supplyresources voted by Parliament in response to Estimates, for expenditure by governmentdepartments.Supply Estimatesa statement of the resources the government needs in the coming financial year, and forwhat purpose(s), by which Parliamentary authority is sought for the planned level ofexpenditure and income.Target rate of returnthe rate of return required of a project or enterprise over a given period, usually at least a year.Third sectorprivate sector bodies which do not act commercially,including charities,social and voluntaryorganisations and other not-for-profit collectives. See annex 7.7.Total Managed a Treasury budgeting term which covers all current and capital spending carried out by the Expenditure,TMEpublic sector (ie not just by central departments).Trading fundan organisation (either within a government department or forming one) which is largely orwholly financed from commercial revenue generated by its activities. Its Estimate shows itsnet impact, allowing its income from receipts to be devoted entirely to its business.Treasury Minutea formal administrative document drawn up by the Treasury, which may serve a wide varietyof purposes including seeking Parliamentary approval for the use of receipts asappropriations in aid, a remission of some or all of the principal of voted loans, andresponding on behalf of the government to reports by the Public Accounts Committee(PAC).62Managing Public Money————————————————————————————————————————GLOSSARY63Managing Public MoneyValue for moneythe process under which organisation’s procurement, projects and processes aresystematically evaluated and assessed to provide confidence about suitability, effectiveness,prudence,quality,value and avoidance of error and other waste,judged for the public sectoras a whole.Virementthe process through which funds are moved between subheads such that additionalexpenditure on one is met by savings on one or more others.Votethe process by which Parliament approves funds in response to supply Estimates.Voted expenditureprovision for expenditure that has been authorised by Parliament. Parliament ‘votes’authority for public expenditure through the Supply Estimates process. Most expenditureby central government departments is authorised in this way.Wider market activity activities undertaken by central government organisations outside their statutory duties,using spare capacity and aimed at generating a commercial profit. See annex 7.6.Windfallmonies received by a department which were not anticipated in the spending review.———————————————————————————————————————— -
15 tension de rétablissement
- восстанавливающееся напряжение (для контактора и пускателя)
- восстанавливающееся напряжение
- восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса коммутационного аппарата или плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока..
Примечания
1 Напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем — промышленной частоты.
2 Определение действительно для однополюсного аппарата. Для многополюсного аппарата — это межфазное напряжение на входных выводах аппаратов.
МЭК 60050(441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule.
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
восстанавливающееся напряжение
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- выключатель, переключатель
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
- cleaning voltage
- recovery voltage
- restoring voltage
- restriking voltage
- transient recovery voltage
- TRV
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
3 У вакуумного контактора или пускателя наибольшее восстанавливающееся напряжение возможно не на первом отключаемом полюсе
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030.4.1-2002 (МЭК 60947-4-1-2000)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > tension de rétablissement
-
16 wiederkehrende Spannung
- восстанавливающееся напряжение (для контактора и пускателя)
- восстанавливающееся напряжение
- восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса коммутационного аппарата или плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока..
Примечания
1 Напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем — промышленной частоты.
2 Определение действительно для однополюсного аппарата. Для многополюсного аппарата — это межфазное напряжение на входных выводах аппаратов.
МЭК 60050(441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule.
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
восстанавливающееся напряжение
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- выключатель, переключатель
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
- cleaning voltage
- recovery voltage
- restoring voltage
- restriking voltage
- transient recovery voltage
- TRV
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
3 У вакуумного контактора или пускателя наибольшее восстанавливающееся напряжение возможно не на первом отключаемом полюсе
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030.4.1-2002 (МЭК 60947-4-1-2000)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > wiederkehrende Spannung
-
17 recovery voltage
- установившееся напряжение
- послеаварийное напряжение
- напряжение восстановления
- восстанавливающееся напряжение (для контактора и пускателя)
- восстанавливающееся напряжение
- восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
- возвращающееся напряжение
возвращающееся напряжение
Напряжение после переходных процессов.
МЭК 60050(441-17-27).
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)
возвращающееся напряжение
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]EN
power frequency recovery voltage
the recovery voltage after the transient voltage phenomena have subsided
[IEV number 441-17-27]FR
tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle
tension de rétablissement après la disparition des phénomènes transitoires de tension
[IEV number 441-17-27]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса коммутационного аппарата или плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока..
Примечания
1 Напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем — промышленной частоты.
2 Определение действительно для однополюсного аппарата. Для многополюсного аппарата — это межфазное напряжение на входных выводах аппаратов.
МЭК 60050(441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030. 1-2000 ( МЭК 60947-1-99)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule.
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50345-99( МЭК 60898-95)]
восстанавливающееся напряжение
-
[Лугинский Я. Н. и др. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике. 2-е издание - М.: РУССО, 1995 - 616 с.]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
- выключатель, переключатель
- высоковольтный аппарат, оборудование...
EN
- cleaning voltage
- recovery voltage
- restoring voltage
- restriking voltage
- transient recovery voltage
- TRV
DE
FR
восстанавливающееся напряжение
Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
Примечания
1 Это напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых напряжение переходное, а на последующем втором — напряжение промышленной частоты.
2 Это определение действительно для однополюсного выключателя. Для многополюсного выключателя — это напряжение между входными выводами аппарата
3 У вакуумного контактора или пускателя наибольшее восстанавливающееся напряжение возможно не на первом отключаемом полюсе
(МЭС 441-17-25)
[ ГОСТ Р 50030.4.1-2002 (МЭК 60947-4-1-2000)]EN
recovery voltage
the voltage which appears across the terminals of a pole of a switching device or a fuse after the breaking of the current
NOTE – This voltage may be considered in two successive intervals of time, one during which a transient voltage exists, followed by a second one during which the power frequency or the steady-state recovery voltage alone exists.
[IEV number 441-17-25]FR
tension de rétablissement
tension qui apparaît entre les bornes d'un appareil de connexion ou d'un fusible après l'interruption du courant
NOTE – Cette tension peut être considérée durant deux intervalles de temps consécutifs, l'un durant lequel existe une tension transitoire, suivi par un second intervalle durant lequel la tension de rétablissement à fréquence industrielle ou en régime établi existe seule
[IEV number 441-17-25]Тематики
EN
DE
FR
послеаварийное напряжение
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
3.26 напряжение восстановления (recovery voltage): Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока.
Это напряжение может рассматриваться в течение двух последовательных промежутков времени, во время первого из которых существует только напряжение переходного процесса, а во время второго промежутка времени - только напряжение восстановления промышленной частоты или напряжение восстановления при установившемся режиме цепи.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60127-1-2005: Миниатюрные плавкие предохранители. Часть 1. Терминология для миниатюрных плавких предохранителей и общие требования к миниатюрным плавким вставкам оригинал документа
3.4.11 восстанавливающееся напряжение (recovery voltage): Восстанавливающееся напряжение в период, когда оно носит существенно переходный характер.
[МЭК 60050 (442-01-05), модифицированный]
Примечание - Это напряжение может рассматриваться в течение двух последовательных промежутков времени, во время первого из которых существует переходное восстанавливающееся напряжение, а во время последующего второго промежутка существует только возвращающееся напряжение промышленной частоты.
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60755-2012: Общие требования к защитным устройствам, управляемым дифференциальным (остаточным) током оригинал документа
3.2.7 установившееся напряжение (recovery voltage); Urec: Максимально допустимое значение установившегося напряжения для особых условий нагрузки.
Примечание - Установившееся напряжение, как правило, выражаемое в процентах номинального напряжения, должно находиться в пределах зоны допуска установившегося напряжения DU. При перегрузке установившееся напряжение ограничивается режимом насыщения скоростью действия регулятора возбуждения (приложение А, рисунок А.1).
Источник: ГОСТ Р 53986-2010: Электроагрегаты генераторные переменного тока с приводом от двигателя внутреннего сгорания. Часть 3. Генераторы переменного тока оригинал документа
3.5.8 восстанавливающееся напряжение (recovery voltage): Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса автоматического выключателя после отключения тока.
[МЭС 441-17-25]
Источник: ГОСТ Р 50345-2010: Аппаратура малогабаритная электрическая. Автоматические выключатели для защиты от сверхтоков бытового и аналогичного назначения. Часть 1. Автоматические выключатели для переменного тока оригинал документа
2.3.23 восстанавливающееся напряжение (recovery voltage): Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока.
Примечание - Это напряжение можно рассматривать в двух последовательных интервалах времени: первый - когда имеется переходное напряжение (см. 2.3.23.1), за которым следует второй - когда имеется только восстанавливающееся напряжение либо промышленной частоты, либо постоянного тока (см. 2.3.23.2).
[МЭС 441-17-25, с изменением]
Источник: ГОСТ Р МЭК 60269-1-2010: Предохранители низковольтные плавкие. Часть 1. Общие требования оригинал документа
3.15.16 восстанавливающееся и возвращающееся напряжение (recovery voltage): Напряжение, появляющееся на выводах полюса коммутационного устройства или плавкого предохранителя после отключения тока.
[МЭК 60050(441-17-25)]
Примечания
1 Напряжение можно рассматривать на протяжении двух последовательных интервалов времени, на первом из которых - переходное напряжение, на последующем - промышленной частоты.
2 Определение действительно для однополюсного устройства. Для многополюсного устройства - это межфазное напряжение на входных выводах устройства.
Источник: ГОСТ Р 51731-2010: Контакторы электромеханические бытового и аналогичного назначения оригинал документа
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > recovery voltage
-
18 transition tension constante à courant constant
переход от постоянного напряжения к постоянному току
-
[IEV number 314-05-09]EN
constant voltage to constant current crossover
behaviour of a stabilized power supply that automatically converts the mode of operation from voltage stabilization to current stabilization when the output current reaches a preset value, and vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]FR
transition tension constante à courant constant
comportement d'une alimentation qui convertit automatiquement le régime de stabilisation en tension en régime de stabilisation en courant lorsque le courant de sortie atteint une valeur préréglée et vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Франко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > transition tension constante à courant constant
-
19 Konstantspannung-Konstantstrom-Kennlinienumschaltung
переход от постоянного напряжения к постоянному току
-
[IEV number 314-05-09]EN
constant voltage to constant current crossover
behaviour of a stabilized power supply that automatically converts the mode of operation from voltage stabilization to current stabilization when the output current reaches a preset value, and vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]FR
transition tension constante à courant constant
comportement d'une alimentation qui convertit automatiquement le régime de stabilisation en tension en régime de stabilisation en courant lorsque le courant de sortie atteint une valeur préréglée et vice versa
Source: 551-19-08
[IEV number 314-05-09]Тематики
- измерение электр. величин в целом
EN
DE
FR
Немецко-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > Konstantspannung-Konstantstrom-Kennlinienumschaltung
-
20 PF
- формирователь импульсов
- фильтр предварительной очистки
- фильтр грубой очистки
- снарядный режим течения (двухфазного потока)
- силовой предохранитель
- потокораспределение
- плоский торец
- отказ элемента (системы)
- отказ детали (оборудования)
- коэффициент мощности
- вентилятор для продувки
вентилятор для продувки
(напр. рукавов рукавного фильтра на ТЭС)
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
коэффициент мощности
Скалярная величина, равная отношению активной мощности двухполюсника к полной мощности.
[ ГОСТ Р 52002-2003]
коэффициент мощности (цепи)
Отношение активного сопротивления к полному сопротивлению при промышленной частоте в эквивалентной цепи, которая считается состоящей из последовательно соединенных индуктивного и активного сопротивлений
[ ГОСТ Р 52565-2006]EN
power factor
under periodic conditions, ratio of the absolute value of the active power P to the apparent power S:
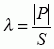
NOTE – Under sinusoidal conditions, the power factor is the absolute value of the active factor.
[IEV ref 131-11-46]FR
facteur de puissance, m
en régime périodique, rapport de la valeur absolue de la puissance active P à la puissance apparente S:
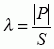
NOTE – En régime sinusoïdal, le facteur de puissance est la valeur absolue du facteur de puissance active.
[IEV ref 131-11-46]
Для синусоидального тока коэффициент мощности равен косинусу угла сдвига фаз между напряжением и током, т. е. равен Cos φ.
После того, как стали массово применяться такие нелинейные нагрузки, как компьютеры и другое офисное и телекоммуникационное оборудование, термин коэффициент мощности перестал быть синонимом термина Cos φ.Тематики
- качество электрической энергии
- электромагнитная совместимость
- электроснабжение в целом
- электротехника, основные понятия
Близкие понятия
Действия
Синонимы
EN
DE
FR
отказ детали (оборудования)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
отказ элемента (системы)
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
EN
потокораспределение
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
ГОСТ 17242-86 - Предохранители плавкие силовые низковольтные. Общие технические условия.

Плавкий силовой предохранительПараллельные тексты EN-RU
Power fuses are suitable for the protection from a short-circuit, Overload current will not protected.
[LS Industrial SystemsСиловые предохранители предназначены для защиты от короткого замыкания и не защищают от токов перегрузки.
[Перевод Интент]LS current limiting power fuse can protect the devices and systems from fault current by interrupting within half cycle.
[LS Industrial Systems]Токоограничивающие плавкие силовые предохранители LS защищают аппараты и системы от тока короткого замыкания размыканием цепи в течение полупериода.
[Перевод Интент]LS Prime-MEC power fuses are designed to protect equipments from fault current such as short-circuit, and generally used for the protection the circuits of transformers, capacitors and motors they protect.
[LS Industrial Systems]Силовые предохранители LS Prime-MEC предназначены для защиты оборудования от токов неисправности, таких как короткое замыкание, и в основном применяются для защиты цепей трансформаторов, конденсаторов и электродвигателей.
[Перевод Интент]Power fuses for combination with vacuum contactors.
[LS Industrial Systems]Силовые предохранители, комбинируемые с вакуумными контакторами
[Перевод Интент]Power fused type vacuum contactors, in-house tested according to IEC 60282-1, can provide short-circuit protection up to 40kA.
[LS Industrial Systems]Контакторы, комбинированные с плавкими силовыми предохранителями, испытаны в соответствии с МЭК 60282-1 и обеспечивают защиту от токов короткого замыкания до 40 кА.
[Перевод Интент]Power fuses can be installed into combination (G, GB) type contactors for the protection of equipments and systems from short-circuit.
[LS Industrial Systems]Для защиты оборудования и систем от короткого замыкания контакторы с вариантом установки G и GB можно комбинировать с силовыми плавкими предохранителями.
[Перевод Интент]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
- PF
- power fuse
Смотри также
снарядный режим течения (двухфазного потока)
поршневой режим течения
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
фильтр предварительной очистки
фильтр грубой очистки
—
[А.С.Гольдберг. Англо-русский энергетический словарь. 2006 г.]Тематики
Синонимы
EN
формирователь импульсов
—
[Я.Н.Лугинский, М.С.Фези-Жилинская, Ю.С.Кабиров. Англо-русский словарь по электротехнике и электроэнергетике, Москва, 1999 г.]Тематики
- электротехника, основные понятия
EN
Англо-русский словарь нормативно-технической терминологии > PF
СтраницыСм. также в других словарях:
Regime theory — is a theory within international relations derived from the liberal tradition that argues that international institutions or regimes affect the behavior of states (or other international actors). It assumes that cooperation is possible in the… … Wikipedia
Current sea level rise — This article is about the current and future rise in sea level associated with global warming. For sea level changes in Earth s history, see Sea level#Changes through geologic time. Sea level measurements from 23 long tide gauge records in… … Wikipedia
regime — noun 1 system of government ADJECTIVE ▪ new ▪ old ▪ Crowds celebrated the downfall of the old regime. ▪ current, established, existing … Collocations dictionary
current — {{Roman}}I.{{/Roman}} noun 1 continuous flowing movement of water ADJECTIVE ▪ fast, fast flowing, powerful, strong, swift ▪ cold, warm ▪ … Collocations dictionary
Current senior Australian Defence Organisation personnel — This page provides access to information about current senior Australian Defence Organisation personnel.[1] The Australian Defence Organisation (ADO) consists of both the uniformed military, known as the Australian Defence Force (ADF), and the… … Wikipedia
Current Labour government (UK) — This article covers aspects of the current Labour government from 1997 under Tony Blair (1997 2007) to today under Gordon Brown.BackgroundLabour was elected in a landslide victory over John Major s Conservative government, which had become deeply … Wikipedia
Current controversies regarding the Presbyterian Church (USA) — The General Assembly of the Presbyterian Church (U.S.A.) adopted a policy of phased, selective divestment from certain American corporations operating in Israel beginning in 2004, as a means of influencing the government of Israel [… … Wikipedia
Dynamic treatment regime — In medical research, a dynamic treatment regime (DTR) or adaptive treatment strategy is a set of rules for choosing effective treatments for individual patients. The treatment choices made for a particular patient are based on that individual s… … Wikipedia
Portal:Current events — Worldwide current events | Sports events … Wikipedia
Covert United States foreign regime change actions — History of the United States This article is part of a series United States Portal … Wikipedia
New Regime (band) — New Regime Anthony Gallo guitarist for New Regime. Background information Origin S.F.V California, United States Genre … Wikipedia
Перевод: со всех языков на русский
с русского на все языки- С русского на:
- Все языки
- Со всех языков на:
- Все языки
- Английский
- Испанский
- Итальянский
- Немецкий
- Русский
- Французский
